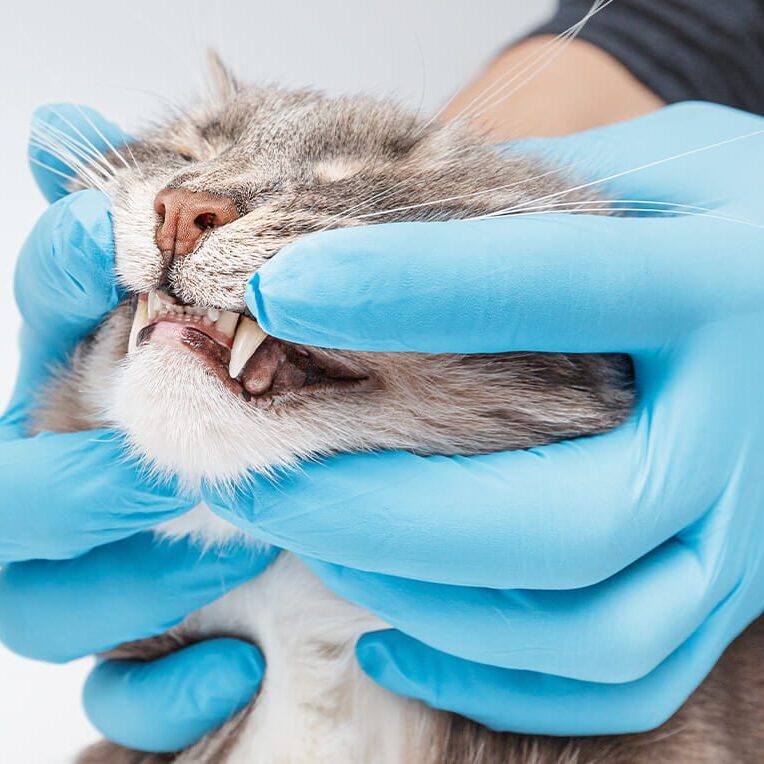
STEP 1: SUPRAGINGIVAL CLEANING
The tartar and plaque that is visible above the gum line is removed so that all surfaces of each tooth may be visualized.
STEP 2: SUBGINGIVAL CLEANING
This is cleaning the area under the gum line. In our animal patients, this is the most important step. The subgingival plaque and calculus is what causes periodontal disease. This is the most common ailment diagnosed in ALL animal patients. Cleaning the tooth surface above the gum line will make the teeth look nice, but in reality does little medically for the patient.
STEP 3: ASSESSMENT
The veterinarian evaluates the entire oral cavity and records any abnormalities on a special dental record. Some examples of oral abnormalities are: tongue or lip lesions, deep pockets in the gums around the teeth and loose, broken or discolored teeth.
STEP 4: ADVANCED DENTAL IMAGING
Advanced Dental Imaging is taken of every tooth in the mouth to discover problems, such as retained roots, enamel defects, root abscesses and bone loss due to infection.
STEP 5: POLISHING
The mechanical removal of the plaque and calculus causes microscopic roughening of the tooth surface. This roughening increases the retentive ability of the tooth for plaque and calculus. Polishing will smooth the surface and decrease the adhesive ability of plaque.
STEP 6: SUB-GINGIVAL LAVAGE
The scaling and polishing of the teeth will cause a lot of debris to become trapped under the gums. This will cause local inflammation, as well as increase the chance of future periodontal disease. For this reason, we gently flush the gingiva with an antibacterial solution.
STEP 7: FLUORIDE TREATMENT
The benefit of fluoride is that it strengthens enamel, decreases tooth sensitivity and is reported to slow the formation of Feline Oral Resorptive Lesions thanks to its anti-plaque qualities. Fluoride can be toxic if swallowed by dogs and cats; therefore, we carefully remove any excess fluoride from the mouth before waking your pet.
STEP 8: TREATMENTS
If any abnormalities were found during the assessment and Dental Advanced Imaging, various treatments may be recommended. Some examples of treatments are: tooth extraction, bonded sealants of fractures and local antibiotic treatment of pockets around the teeth. The veterinarian will explain any abnormalities and discuss treatment options. We are happy to provide an estimate at each stage of this procedure.
STEP 9: PREVENTION
Prevention is one of the most important parts of the oral hygiene procedure.